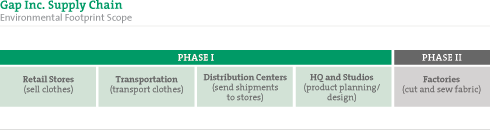
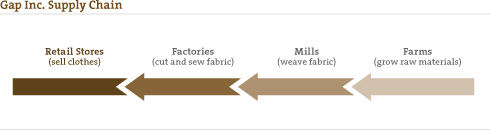
Nowadays, when it comes to cotton, you can pretty much take your ‘pick’: low-chemical, organic, low-water use, fair trade, conventional. So what’s all the hype this week about organic cotton? Well, Organic Exchange released their 2007-2008 Organic Cotton Market Report.
According to this article:
“Global retail sales of organic cotton apparel and home textile products climbed 63 percent in 2008 to $3.2 billion […]
‘Despite the global retail outlook, most brands and retailers selling organic cotton products remain committed to their sustainability plans and upbeat about market growth with plans to expand their product lines 24 and 33 percent in 2009 and 2010, respectively, to result in an estimated $4 billion market in 2009 and a $5.3 billion market in 2010,’ the report said.
The amount of organic cotton farmers grew worldwide in 2007/08 increased 152 percent, according to the 2008 Organic Cotton Farm and Fiber Report.
The amount hit 145,872 metric tons, which is equivalent to 668,581 (480-lb.) bales. It was grown on 161,000 hectares (400,000 acres) in 22 countries worldwide.
Organic production is based on a system of farming that maintains and replenishes soil fertility without using pesticides, fertilizers or genetically modified seeds.”
Keep in mind, just because the cotton is certified organic, doesn’t necessarily make it the best defence against the many negative effects of conventional cotton.
Take, for example, the Sustainable Cotton Project (SCP). The low-chemical system of biological integrated pest management (IPM) helps farmers reduce chemical usage at a much larger scale than what would be achieved through a smaller number of completely organic cotton farms. This approach looks toward the overall impact of the sector, rather than just on one farm at a time. To help growers and consumers make sense of the difference, the project has developed an online calculator. Buyers and growers can use the calculator as a means of comparing the ecological footprint of BASIC (biological agricultural systems in cotton) against conventional cotton. The ecological calculator measures land, water and carbon footprints. I haven’t used the calculator (as I am neither a cotton buyer nor grower) and would like to welcome anyone who has used it, or who is interested in using it, to leave a comment with some feedback on the success/failure of the SCP initiative. What impresses me most about SCP is their involvement in sustainable fashion design education. Based out of California, the SCP initiative has partnered with California College of the Arts and The Academy of Art educating fashion design students in the area of sustainable design through the BASIC program. This is exciting.
Social Impact?
Missing from most footprint calculators is a fibre’s social impact. But, how do you measure a social footprint? How do you measure happiness? Certified Fairtrade cotton is not always organic, so what is it?
According to the Fairtrade Foundation
“The Mark is an independent product certification label which guarantees that cotton farmers are getting a better deal – receiving a fair and stable Fairtrade price and Fairtrade premium, receiving pre-financing where requested and benefiting from longer-term, more direct trading relationships.
The Fairtrade minimum price is set at the farm gate level and is based on actual costs of sustainable production. If the local market price is higher than this minimum price, then the market price applies. An additional payment of a Fairtrade premium is set aside for farmers’ organisations to spend on social and environmental projects or to strengthen their businesses. This ensures that communities have the power and resources to invest in long-term improvements. Elected farmer committees decide democratically how these premiums are spent.”
Organic Cotton ≠ Fair Trade Cotton: Responsible fashion is not just about being ‘organic’.
“All Fairtrade certified cotton producers are required to demonstrate increased diligence in choosing appropriate non-harmful chemicals or a biological or home-made alternative wherever possible. As would be expected, farmers are prohibited from using pesticides in the Pesticide Action Network’s “dirty dozen” list and those in the FAO/UNEP’s Prior Informed Consent Procedure list.”
According to Kate Fletcher, “[t]he total area of land dedicated to cotton growing has not changed significantly for around 80 years, but in that time output has tripled” (8). Fletcher directly associates the increase in production to a swell in pesticide and fertilizer use, and recommends organic, low chemical, hand-picked, rain-fed, or drip-irrigated cotton as alternatives, or using hemp or flax as a fibre substitution (9). A rise in consumer awareness about the negative effects of conventional cotton on the environment has no doubt created the business case for companies to begin to source organic cotton.
Top 10 companies:
1. Wal-Mart (USA)
2. C&A (Belgium)
3. Nike (USA)
4. H&M (SE)
5. Zara (Spain)
6. Anvil (USA)
7. Coop Switzerland
8. Pottery Barn (USA)
9. Greensource (USA)
10. Hess Natur (Germany).
But how have companies such as these been able to incorporate organic cotton into their production lines? According to Fletcher, “[u]nlike more politically contentious and technically challenging ‘alternative’ fibres such as hemp, organic cotton fibre is a fairly straightforward like-for-like substitute for conventionally grown cotton” (21). And what stands in the way of an increased use in organic cotton? Apparently the answer is supply. According to Fletcher, “organic cotton makes up a tiny percentage (0.18 per cent) of the world fibre demand and around 1 per cent of the total cotton market.” (21)
So what does all this mean? When searching for sustainable fibres make sure to consider the entire lifecycle of that fibre (both environmental and social). Eliminating pesticide use is only part of the solution. Let’s not forget to think outside the crop.
Source: Greenbiz, Fairtrade, Reuters, SCP and Sustainable Fashion & Textiles: Design Journeys, by Kate Fletcher

 Veja soles are made of natural latex coming straight from the Amazon Forest in the Chico Mendes reserve. The Amazon is the only place on earth where wild rubber trees are to be found […] Their activity, which does not require putting down any tree, is a great way to preserve the world’s largest forest. Natural rubber is renewable and biodegradable, as opposed to synthetic rubber or plastic, which is produced by using fossil and non-renewable materials.
Veja soles are made of natural latex coming straight from the Amazon Forest in the Chico Mendes reserve. The Amazon is the only place on earth where wild rubber trees are to be found […] Their activity, which does not require putting down any tree, is a great way to preserve the world’s largest forest. Natural rubber is renewable and biodegradable, as opposed to synthetic rubber or plastic, which is produced by using fossil and non-renewable materials.